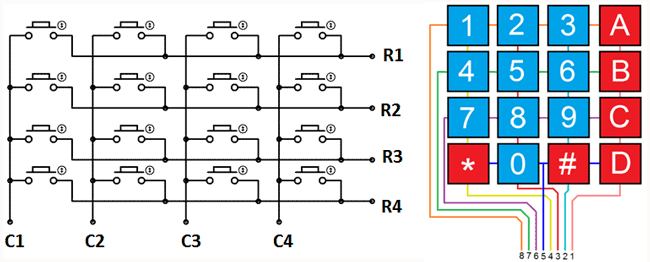
Matrix Keypad
Matrix Keypads are commonly used in calculators, telephones etc where a number of input switches are required. We know that matrix keypad is made by arranging push button switches in row and columns. In the straight forward way to connect a 4×4 keypad (16 switches) to a microcontroller we need 16 inputs pins. But by connecting switches in the following way we can read the status of each switch using 8 pins of the microcontroller.
The status of each keys can be determined by a process called Scanning. For the sake of explanation lets assume that all the column pins (Col1 – Col4) are connected to the inputs pins and all the row pins are connected to the output pins of the microcontroller. In the normal case all the column pins are pulled up (HIGH state) by internal or external pull up resistors. Now we can read the status of each switch through scanning.
- A logic LOW is given to Row1 and others (Row2 – Row-4) HIGH
- Now each Column is scanned. If any switch belongs to 1st row is pressed corresponding column will pulled down (logic LOW) and we can detect the pressed key.
- This process is repeated for all rows.
#include<reg51.h>
sbit rs = P3^5;
sbit e = P3^6;
void delay(unsigned int x)
{
while(x--);
}
void cmd(unsigned char c)
{
P3 = c;
rs = 0;
rw = 0;
e = 1;
delay(50);
e = 0;
}
void dat(unsigned char b)
{
P3 = b;
rs = 1;
rw = 0;
e = 1;
delay(50);
e = 0;
}
void lcd()
{
cmd(0x38);
delay(300);
cmd(0x80);
delay(300);
cmd(0x0E);
delay(300);
cmd(0x01);
delay(300);
}
void main()
{
int a,b,c;
lcd();
while(1)
{
P1 = 0x0F;
while(P1 == 0x0F);
a = P1;
P1 = 0xF0;
b = P1;
while(P1!=0xF0);
c = a+b;
if(c==0xE7)
{
dat('7')
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xEB)
{
dat('8')
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xED)
{
dat('9');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xEE)
{
dat('/');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xD7)
{
dat('4');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xDB)
{
dat('5');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xDD)
{
dat('6');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xDE)
{
dat('*');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xB7)
{
dat('1');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xBB)
{
dat('2');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xBD)
{
dat('3');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0xBE)
{
dat('-');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0x77)
{
dat('C');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0x7b)
{
dat('0');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else if(c==0x7D)
{
dat('=');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
else
{
dat('+');
delay(60000);
cmd(0x01);
}
}
}
Interfacing keypad with 8051 microcontroller (AT89S52)
The same code simulated in Proteus looks like this:


No comments:
Post a Comment